Habits are the autopilot of our lives, but what keeps them running smoothly? The answer lies in the complex interplay of neural pathways and chemicals, with dopamine playing a starring role.

More details of dopamine and habit formation
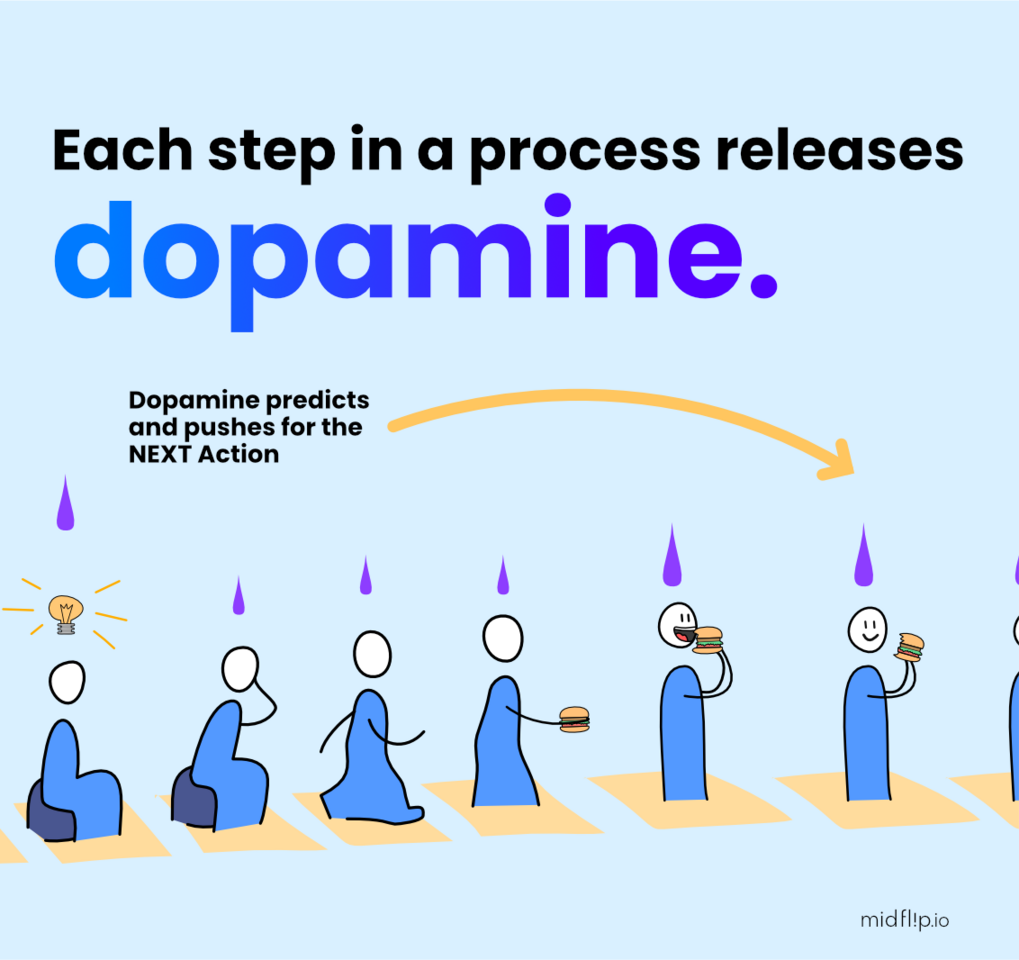
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that helps regulate motivation, reward, and reinforcement learning. While it's not the sole factor in habit formation, it plays a crucial role in strengthening the neural connections that underlie our routines. Here's a closer look:
Reward-Driven Learning
Dopamine is released when we experience rewarding outcomes
This dopamine signal helps the brain learn which actions lead to positive results
Over time, this reinforces the neural pathways associated with the rewarding behavior
Motivational Salience
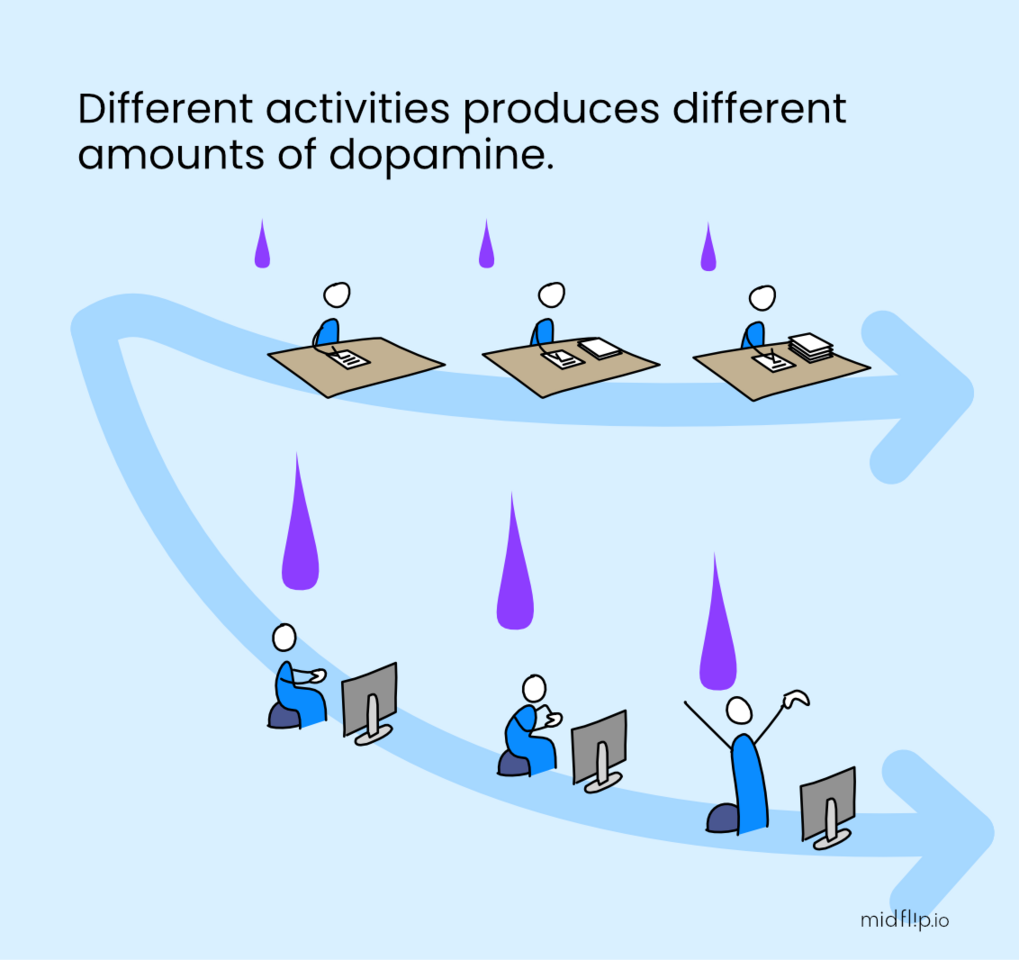
Dopamine increases the motivational salience of cues related to rewards
This means that dopamine can make certain cues or stimuli more attention-grabbing and desirable
This motivational effect can contribute to the drive to engage in habitual behaviors
Habit Reinforcement
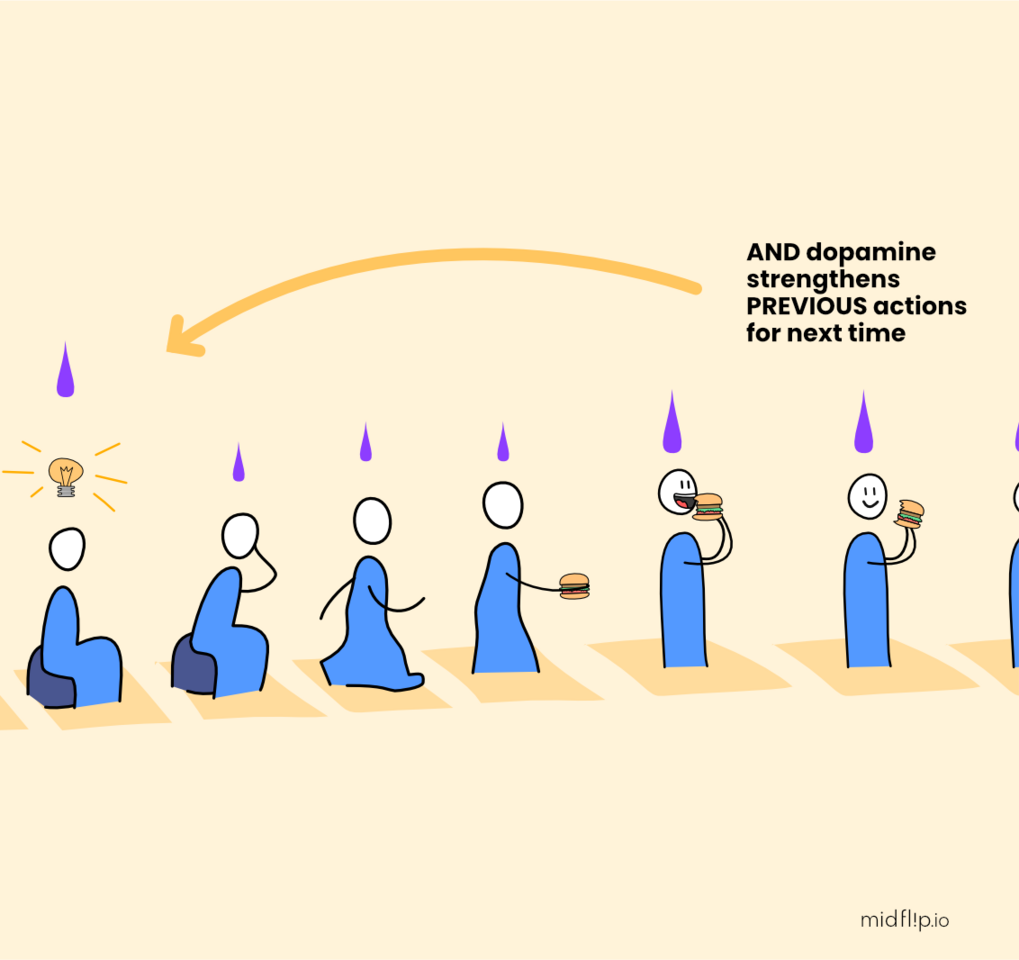
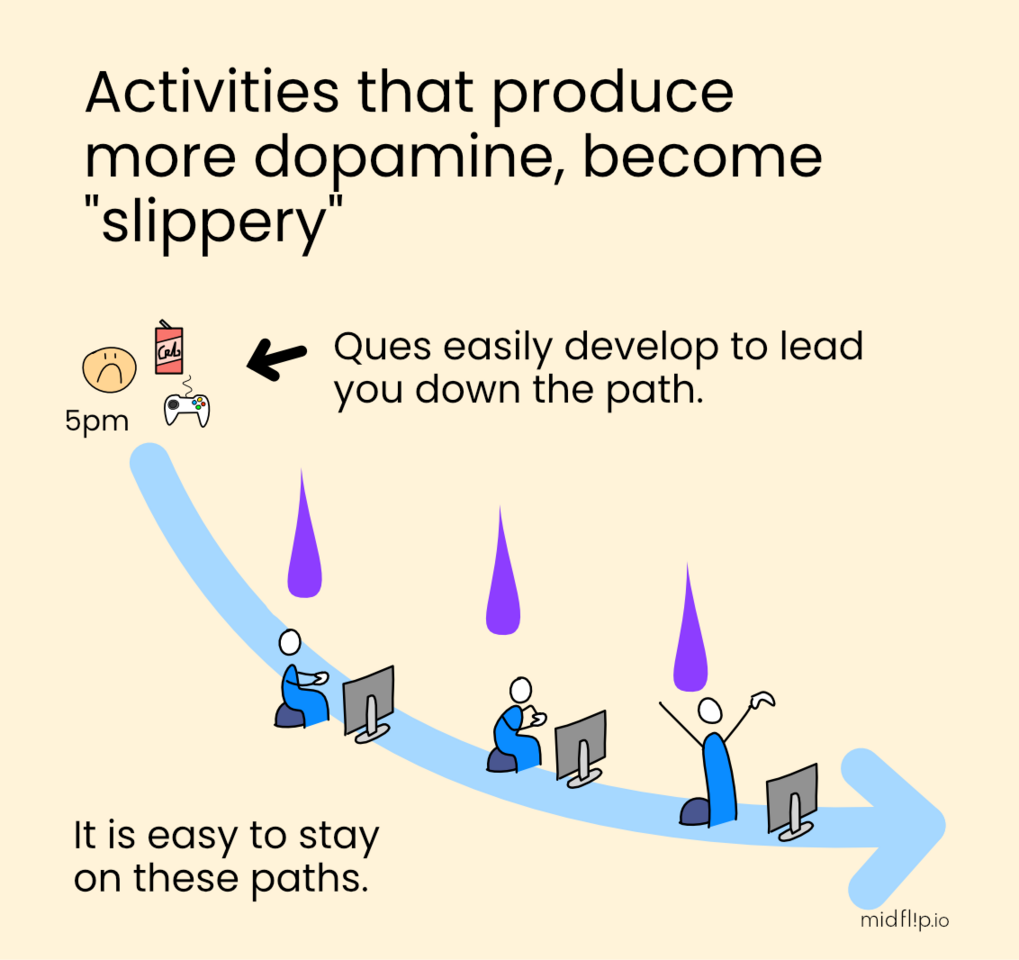
Repeated engagement in a rewarding behavior strengthens the associated neural pathways
Dopamine plays a role in this reinforcement process, helping to solidify the habit loop
However, habit formation also involves other neurotransmitters and brain regions beyond just dopamine
While dopamine is involved in reinforcing habits, it's not the only factor to consider when trying to change them. Habit change involves a complex interplay of behavioral, cognitive, and environmental factors. Honestly, in the details, its complicated as all hell. If you know more and can explain it well. Write it out here!


Set your environment
Setting up your environment is probably the best strategy to stop unwanted habits. It can be hard to implement, especially if you do not have much control over your environment.
So, you intentionally modify your surroundings to remove triggers that prompt undesired behaviors. For instance, if you're trying to reduce snacking, you would:
By creating an environment that supports your goals, you make it easier to avoid temptation and stick to positive behaviors, effectively reducing the willpower needed to resist old habits.

Habit Stacking
Habit stacking is a technique for building new habits by anchoring them to existing routines. The idea is simple: you take a habit you already do consistently and use it as a trigger to add a new, desired behavior. For example, if you always brush your teeth in the morning, you might stack a new habit of doing 10 push-ups right after. By linking the new habit to an established one, you leverage your brain's existing neural pathways, making it easier to remember and perform the new action. This method reduces the mental effort required to form new habits and increases the likelihood of long-term success.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that helps regulate motivation, reward, and reinforcement learning. While it's not the sole factor in habit formation, it plays a crucial role in strengthening the neural connections that underlie our routines. Here's a closer look:
Reward-Driven Learning
Dopamine is released when we experience rewarding outcomes
This dopamine signal helps the brain learn which actions lead to positive results
Over time, this reinforces the neural pathways associated with the rewarding behavior
Motivational Salience
Dopamine increases the motivational salience of cues related to rewards
This means that dopamine can make certain cues or stimuli more attention-grabbing and desirable
This motivational effect can contribute to the drive to engage in habitual behaviors
Habit Reinforcement
Repeated engagement in a rewarding behavior strengthens the associated neural pathways
Dopamine plays a role in this reinforcement process, helping to solidify the habit loop
However, habit formation also involves other neurotransmitters and brain regions beyond just dopamine
Modulating Habit Change
While dopamine is involved in reinforcing habits, it's not the only factor to consider when trying to change them
Habit change involves a complex interplay of behavioral, cognitive, and environmental factors
Strategies like replacing rewards, modifying cues, and practicing mindfulness can help reshape habits over time
Dopamine is a key player in the habit formation process, but it's part of a larger neural symphony. By understanding the role of dopamine and other factors involved in habit learning, we can develop more effective strategies for cultivating positive habits and breaking negative ones.


Hot comments
about anything